
Launching a website is exciting. You buy a domain, design pages, publish content, and finally hit “live.” Naturally, the next step is to search for your website on Google. But when you do that, nothing appears. Even when you search using site:yourwebsite.com, Google shows no results.
This situation is far more common than most people realize.
If you are asking “how do I get my website indexed by Google?”, it does not mean you have failed at SEO or built your website incorrectly. In most cases, it simply means Google has not yet discovered, crawled, or indexed your site.
Indexing is the foundation of visibility. If your website is not indexed, it cannot rank. If it cannot rank, it cannot receive organic traffic. Every SEO effort—keywords, content, links—depends on indexing happening first.
This guide explains indexing from the ground up. It is written for real website owners, not engineers, and it follows how Google actually works according to official documentation and widely accepted SEO practices. There are no shortcuts, myths, or invented tricks here—only what genuinely helps your website get indexed.
What Does “Indexed by Google” Actually Mean?
When Google indexes a website or a page, it means Google has added that page to its massive database called the Google Index. This index is what Google searches through when someone types a query into the search bar.
Indexing happens after two other processes:
- Discovery – Google becomes aware that a URL exists
- Crawling – Googlebot visits the page and reads its content
Only after crawling does Google decide whether the page deserves to be indexed.
This is an important distinction. A page can be crawled but still not indexed. Google makes indexing decisions automatically based on quality, usefulness, and technical accessibility.
If a page is not indexed:
- It will not appear in search results
- It will not receive organic traffic
- It will not rank, regardless of how good the content is
Indexing is not about ranking position. It is about eligibility.
This is why many beginners ask, how do I get my website indexed by Google, even though their site looks perfectly fine from the outside.
How Google Finds Websites and Pages

Google does not manually review new websites. It relies on automated systems to discover content across the web. According to Google Search Central, Google primarily finds pages in three ways.
Links from Other Websites
Links are the strongest discovery signal. When Google crawls a page that is already indexed and finds a link pointing to a new website, it follows that link and discovers the new URL.
This is why established websites tend to get indexed faster than brand-new ones. They already have links and visibility.
However, backlinks are not mandatory for indexing. They simply speed up discovery.
XML Sitemaps
A sitemap is a file that lists important URLs on your website. It helps search engines understand the structure of your site and discover pages more efficiently.
Google explicitly states that sitemaps are useful for:
- New websites
- Large websites
- Websites with weak internal linking
Submitting a sitemap does not guarantee indexing, but it makes discovery easier and more reliable.
Google Search Console Submissions
Google Search Console is Google’s official tool for website owners. It allows you to submit URLs and sitemaps directly to Google and monitor how Google sees your site.
For new websites, Search Console is the most direct and transparent way to support indexing.
How to Check If Your Website Is Indexed by Google
Before trying to fix anything, you should confirm whether your website or specific pages are indexed.
The simplest method is using the site: search operator.
Type the following into Google:
site:yourwebsite.com
If Google shows results, those pages are indexed. If no results appear, Google has not indexed your site yet.
For more accurate information, use Google Search Console. The URL Inspection tool tells you whether a page is indexed, when it was last crawled, and whether any issues are preventing indexing.
Search Console is the most reliable source because it reflects Google’s internal data, not just public search results.
Why Your Website Is Not Indexed by Google
Indexing issues usually have logical explanations. Most are not penalties or mistakes. Below are the most common reasons Google does not index websites, especially new ones.
When these issues stack up, it becomes clear why so many people search How do I get my website indexed by Google soon after launching a new site.
Your Website Is New
Google itself states that indexing new websites can take time. If your site was launched recently and has few pages or links, delayed indexing is normal.
New websites have:
- Low crawl priority
- Limited trust signals
- Fewer discovery paths
This improves naturally over time as the site grows.
Google Does Not Know Your Website Exists
If you have not:
- Set up Google Search Console
- Submitted a sitemap
- Shared or linked your site anywhere
Google may simply not have discovered your website yet.
A website with no discovery signals can remain invisible for weeks.
Your Pages Are Blocked from Indexing
Sometimes websites unintentionally block Google.
Common causes include:
noindexmeta tags- Incorrect
robots.txtrules - CMS settings that discourage search engines
These signals explicitly tell Google not to index pages, even if they are crawled.
Thin or Low-Value Content
Google does not index every page it crawls. Pages may be excluded if they:
- Contain very little content
- Duplicate other pages
- Offer no clear value to users
This is not a punishment. It is a quality filter.
Poor Internal Linking
If a page has no internal links pointing to it, Google may struggle to discover or prioritize it. Pages that are isolated from the rest of the site are called orphan pages, and they are harder to index.
How Do I Get My Website Indexed by Google? Step-by-Step

If you are wondering How do I get my website indexed by Google without using shortcuts, paid tools, or risky tactics, the steps below follow Google’s own recommendations and widely accepted SEO practices.
Now we move to the practical part. These steps follow Google’s own recommendations and established SEO practices.
Set Up Google Search Console
Google Search Console is essential. It is the official way to communicate with Google about your website.
To set it up:
- Go to Google Search Console
- Add your website as a property
- Verify ownership using DNS, HTML file, or meta tag
Once verified, Google officially recognizes you as the site owner. This alone can help with discovery.
Submit Your XML Sitemap
After setting up Search Console, submit your sitemap.
Most websites have their sitemap at:
https://yourwebsite.com/sitemap.xml
In Search Console:
- Go to “Sitemaps”
- Enter the sitemap URL
- Submit it
This helps Google discover your pages more efficiently.
Request Indexing Using the URL Inspection Tool
For important pages, you can request indexing manually.
Paste the page URL into the URL Inspection tool. If the page is not indexed, click “Request Indexing.”
Google states that this submits the page for priority crawling. However, it does not guarantee indexing. Use this feature selectively.
Check Robots.txt and Noindex Tags
Make sure your website is not blocking Google.
Check that:
robots.txtdoes not disallow Googlebot- Important pages do not contain a
noindexmeta tag
Search Console provides tools to test both.
Improve Internal Linking
Internal links guide Googlebot through your site.
Best practices:
- Link from your homepage to important pages
- Link between related blog posts
- Use descriptive anchor text
Internal links improve both crawlability and indexing priority.
Publish Content Worth Indexing
Google indexes pages it believes are useful.
For new websites, this usually means:
- Clear topic focus
- Original writing
- Enough depth to answer the user’s question
- No copied or spun content
Quality matters more than quantity.
Use External Discovery Signals
While not required, external links help Google discover your site faster.
Simple options include:
- Linking from social profiles
- Sharing posts on platforms like LinkedIn or Twitter
- Adding your site to relevant directories or profiles
These links do not need to be powerful. They simply need to exist.
How Long Does Google Take to Index a Website?
The timeline matters because many site owners start worrying and repeat the same question — How do I get my website indexed by Google — within just a few days of launching.
There is no fixed timeline. Google does not promise specific indexing speeds.
Based on official statements and observed behavior:
- Some pages are indexed within hours
- Others take days or weeks
- Some are never indexed
Indexing speed depends on:
- Site age
- Crawl accessibility
- Content quality
- Internal and external links
For new websites, waiting one to four weeks is common and normal.
How to Index a Website on Google Faster (Safely)
There is no guaranteed way to force indexing, but you can reduce friction.
What helps:
- Submitting a sitemap
- Clean site structure
- Logical internal links
- Avoiding thin or duplicate pages
What does not help:
- Repeated indexing requests
- Paid “instant indexing” services
- Spammy backlinks
- Ping tools claiming guaranteed results
Google discourages manipulation attempts.
Understanding “Discovered – Not Indexed” in Google Search Console
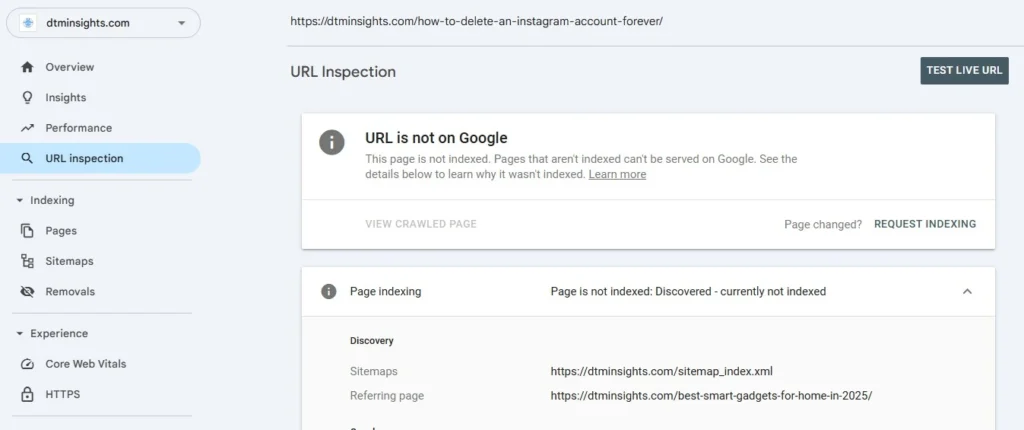
This status often appears right after people learn How do I get my website indexed by Google, submit their site, and then expect instant results.
This status means Google knows the URL exists but has not indexed it yet.
It is not an error.
Common reasons include:
- New site with low priority
- Google evaluating content quality
- Limited crawl budget
In many cases, this resolves on its own over time. Improving content and internal links is usually more effective than repeated requests.
Indexing vs Ranking: A Common Confusion
Indexing and ranking are different.
- Indexed but not ranking means the page exists in Google’s index but appears far down in results.
- Not indexed means the page does not exist in the index at all.
Search Console helps you distinguish between the two. If a page is indexed but not ranking, that is an SEO issue, not an indexing issue.
Read Also This- How to See What Keywords a Site Ranks For
Common Myths About Google Indexing
There are many misconceptions about indexing.
Google does not index every page.
Paid ads do not speed up indexing.
You cannot force Google to index a page.
More pages do not mean faster indexing.
Google’s systems decide what to index based on usefulness and accessibility.
Final Thoughts
In the end, if you keep asking how do I get my website indexed by Google, the answer always comes back to the same fundamentals: access, clarity, and patience.
If you are asking how to get your website indexed by Google, the most important thing to understand is this: indexing is a process, not a button.
Google indexes pages when:
- It can find them
- It can crawl them
- It believes they provide value
Your role is to remove obstacles and create clarity. Once your website is indexed, you can move on to ranking, traffic growth, and long-term SEO strategy.
Indexing is the foundation. Everything else builds on top of it.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I get my website indexed by Google step by step?
To understand how do I get my website indexed by Google, you need to focus on discovery, crawlability, and content quality. Setting up Google Search Console, submitting a sitemap, fixing indexing blocks, and publishing useful content are the core steps.
How do I get my website indexed by Google for free?
Google indexing is always free. You only need Google Search Console and proper site setup.
Why is Google not indexing my website even after submission?
Submission does not guarantee indexing. Content quality, site signals, and time all matter.
How can I submit my website to Google?
By adding your site to Google Search Console and submitting a sitemap.
How long does Google take to index a new website?
Anywhere from a few days to several weeks. There is no fixed timeline.
Can I force Google to index my site?
No. You can request indexing, but Google makes the final decision.




Pingback: How Long Does SEO Take to Show Results in 2026?